The skincare world is transforming, with more people gravitating toward natural and plant-based products. At the forefront of this revolution are herbal extracts, ingredients derived from nature that deliver incredible benefits for your skin. These extracts are full of antioxidants, vitamins, and active compounds that can hydrate, brighten, heal, and protect the skin.
Herbal extracts have been used for centuries in traditional medicine across cultures. From Ayurvedic formulations to ancient Chinese remedies, plants have always been recognised as a source of healing and beauty. Today, advancements in extraction techniques and skincare science allow these age-old ingredients to be more potent and effective than ever.
This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about herbal extracts in skincare, including what they are, manufacturing processes, and their many benefits.

What Are Herbal Extracts?
Herbal extracts are plant solutions with high active concentrations to harness their beneficial properties. These extracts capture the active compounds found in herbs, flowers, roots, or seeds, making them highly potent and effective in skincare formulations.
Key Features of Herbal Extracts:
Rich in Active Ingredients: Contain antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and essential oils that target specific skin concerns.
Natural Origin: Extracted directly from plants without synthetic interference, making them ideal for clean beauty products.
Versatile Applications: Used in serums, moisturisers, cleansers, and even makeup to provide hydration, healing, and protection.
Customizable Benefits: Different extracts address various concerns like dryness, ageing, acne, or hyperpigmentation.
For example, green tea extract is famous for its anti-ageing and antioxidant properties, while chamomile extract is a go-to for soothing sensitive skin. Herbal extracts bridge the gap between natural remedies and scientifically based skincare.

Types of Herbal Extracts
Herbal extracts can be classified based on the solvent and extraction process used, which determines the type of active compounds extracted and their suitability for different skincare formulations. Below is an overview of the various types of herbal extracts most common in the beauty industry:
1. Aqueous Herbal Extracts (Water-Based)
Aqueous extracts are prepared using water as the solvent, typically through processes like boiling, steeping, or soaking. This method is ideal for extracting water-soluble compounds such as vitamins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides. These extracts are lightweight and hydrating, making them suitable for products like toners, gels, and serums. Aloe vera gel is a classic example, known for its soothing and hydrating properties, while green tea extract is famous for its powerful antioxidant benefits. Aqueous extracts are particularly popular in formulations which deliver hydration or combat inflammation.
2. Alcohol-Based Extracts (Tinctures)
Tinctures are herbal extracts made by soaking plant materials in alcohol or a mixture of alcohol and water. Alcohol acts as a potent solvent, effectively extracting bioactive compounds, including alkaloids, tannins, and essential oils. These extracts are highly concentrated and have a long shelf life, making them valuable for preserving the potency of delicate herbs. Chamomile tincture, for instance, is often used for its calming properties, while calendula tincture is incorporated into skincare to aid in wound healing and reduce redness. However, alcohol-based extracts must be used sparingly in skincare formulations to avoid drying effects.

3. Oil-Based Herbal Extracts (Infused Oils)
Oil-based extracts are created by infusing plant materials in carrier oils like olive, jojoba, or sunflower oil. The fat-soluble compounds in herbs, such as vitamins A, D, and E, along with certain antioxidants, dissolve into the oil, producing nutrient-rich extracts. Infused oils are ideal for creating nourishing skincare products, including creams, balms, and body oils. For example, rosehip oil infused with calendula provides anti-inflammatory benefits, while lavender-infused oil promotes relaxation and skin repair. These extracts are particularly suited for dry and sensitive skin types due to their emollient properties.
4. Glycerin-Based Extracts (Glycerites)
Glycerites are herbal extracts made using vegetable glycerin as the solvent. This method is an excellent alternative to alcohol-based extraction, especially for individuals with sensitive skin or who prefer alcohol-free products. Glycerin-based extracts are gentle and moisturising, as glycerin itself acts as a humectant, drawing water into the skin. They are commonly used in cleansers, hydrating toners, and lightweight lotions. For example, cucumber glycerite is often included in formulations to cool and refresh the skin, while chamomile glycerite offers soothing and anti-redness benefits.
5. Powdered Herbal Extracts
Powdered extracts are created by drying and grinding herbal material into a fine powder. These extracts are concentrated and easily incorporated into various formulations, as they dissolve readily in water, oils, or alcohol. Powdered extracts are often used in DIY skincare or as active ingredients in masks, serums, and scrubs. For instance, turmeric powder is widely recognised for its brightening and anti-inflammatory effects, while liquorice root powder helps reduce pigmentation and soothe irritated skin.

6. Essential Oils
Essential oils are highly concentrated extracts obtained through steam distillation or cold pressing. They contain volatile aromatic compounds that give plants their characteristic scents and therapeutic properties. Essential oils are used in small quantities due to their potency and are typically diluted in carrier oils or added to skincare formulations for their aromatherapeutic and skin-benefiting effects. For example, tea tree oil is popular for treating acne, while rose oil is valued for its anti-ageing and hydrating properties.
7. CO2 Extracts
CO2 extracts are produced using supercritical carbon dioxide as a solvent, which allows for the extraction of both volatile and non-volatile compounds. These extracts are incredibly pure and highly concentrated, preserving the full spectrum of active compounds from the plant. CO2 extracts are commonly used in high-end skincare formulations for their potency and stability. For example, sea buckthorn CO2 extract is known for its regenerative and anti-ageing properties, while calendula CO2 extract provides soothing benefits for sensitive skin.
8. Hydroalcoholic Extracts
Hydroalcoholic extracts are a blend of water and alcohol as solvents, combining the strengths of both to extract a wide range of active compounds. This method is particularly effective for plants with diverse phytochemicals, such as flavonoids, tannins, and saponins. These extracts are versatile and commonly used in toners, serums, and other water-based formulations to deliver multi-faceted benefits. Witch hazel extract, for example, is a hydroalcoholic extract that works as a natural astringent and anti-inflammatory agent.
9. Fermented Extracts
Fermentation is an innovative technique where plant materials are fermented using specific microorganisms. This process enhances the bioavailability of the active compounds, making them more easily absorbed by the skin. Fermented extracts are rich in probiotics, enzymes, and amino acids, which help strengthen the skin barrier and improve hydration. Popular examples include fermented green tea for antioxidant protection and fermented rice water for brightening and softening the skin.
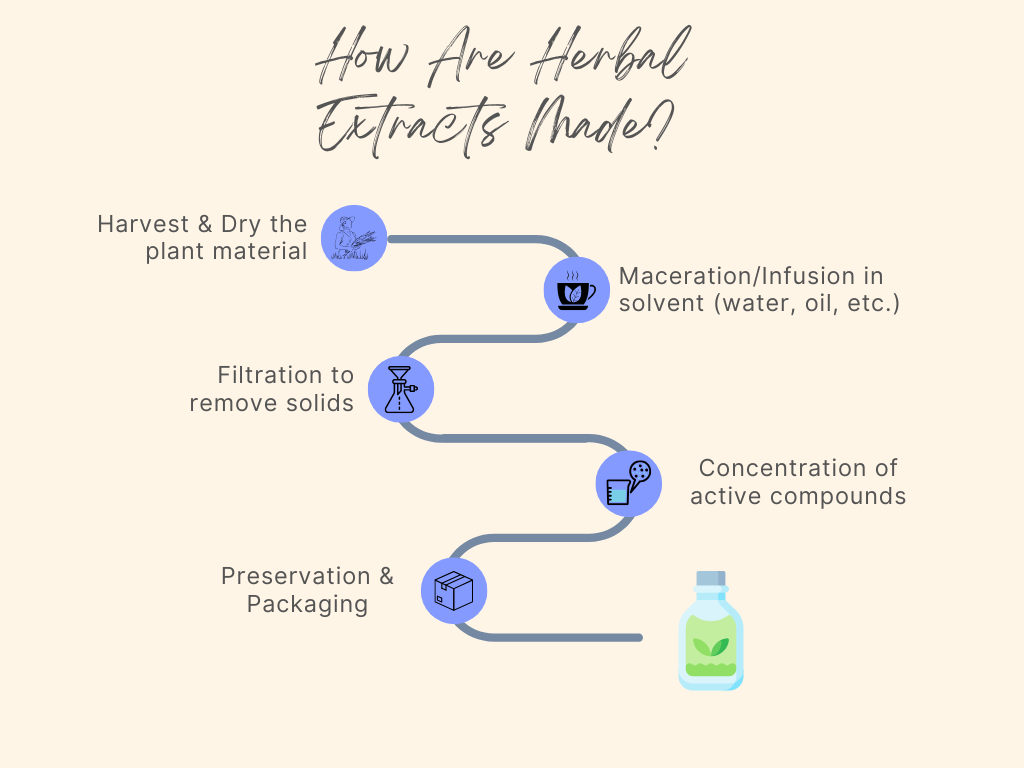
Extraction Techniques
The process of extracting beneficial compounds from herbs is as critical as the herbs themselves. Each technique is tailored to preserve the potency and quality of the desired active ingredients. Below is a detailed look at the various methods used in extracting herbal components for skincare:
1. Maceration
Maceration involves soaking plant material in a solvent (such as water, oil, or alcohol) at room temperature for an extended period to draw out the beneficial compounds. This is one of the simplest methods and is often used for home extractions.
Advantages: Gentle on heat-sensitive compounds, easy to perform.
Common Applications: Infused oils for balms and lotions, or alcohol-based tinctures.
Example: Calendula flowers infused in olive oil to create a soothing salve.
2. Distillation
This method uses heat and steam to separate essential oils and hydrosols (floral waters) from the plant. Distillation preserves volatile compounds like essential oils that can easily evaporate.
Advantages: Produces both essential oils and hydrosols, which are highly concentrated and versatile.
Common Applications: Toners, mists, and aromatherapy oils.
Example: Lavender essential oil distilled from flowers for its calming properties.
3. Cold Pressing
Cold pressing is a mechanical method used to extract oils from seeds, nuts, or fruits without the use of heat. The absence of heat ensures that the nutrients and antioxidants remain intact.
Advantages: Retains the maximum nutritional value of oils.
Common Applications: Used in premium carrier oils like argan, jojoba, or rosehip oil.
Example: Cold-pressed rosehip oil for anti-ageing skincare.
4. Supercritical CO2 Extraction
This advanced technique uses supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2), which acts as both a liquid and a gas under specific pressure and temperature conditions, to extract compounds. It is one of the most efficient and eco-friendly methods available.
Advantages: Produces highly pure and potent extracts without the use of harmful solvents.
Common Applications: Used in premium skincare products for ingredients like sea buckthorn or rosehip extract.
Example: Sea buckthorn CO2 extract, known for its rejuvenating properties.
5. Infusion
Infusion involves steeping herbs in a solvent (typically water or oil) with or without heat. It is a gentle process often used to create therapeutic teas or infused oils.
Advantages: Simple and effective for extracting water- or oil-soluble compounds.
Common Applications: Used in DIY skincare for creating herbal teas or floral waters.
Example: Chamomile tea, used as a toner to calm irritated skin.
6. Digestion
Digestion involves heating the plant material in a solvent at a controlled, low temperature for a prolonged period. The gentle heat accelerates the extraction process without degrading heat-sensitive compounds.
Advantages: Efficient for extracting both heat-sensitive and non-heat-sensitive compounds.
Common Applications: Creating oil or alcohol-based extracts for use in creams or serums.
Example: Digesting rosemary in olive oil to produce an anti-inflammatory extract.
7. Decoction
Decoction is used for tough plant materials like roots, barks, or seeds. The plant material is boiled in water for an extended time to release its active compounds. This method is common in traditional medicine and for preparing strong herbal extracts.
Advantages: Ideal for extracting water-soluble compounds from harder plant parts.
Common Applications: Creating herbal tonics and concentrated extracts.
Example: Boiling liquorice root to create a brightening skin extract.
8. Percolation
Percolation involves continuously passing a solvent (like water or alcohol) through powdered plant material in a specialised apparatus. The solvent slowly dissolves the active compounds as it flows through the plant material.
Advantages: Produces highly concentrated extracts quickly.
Common Applications: Creating tinctures and liquid concentrates for skincare formulations.
Example: Percolating echinacea for an extract with soothing and healing properties.
9. Soxhlet Extraction
Soxhlet extraction is a laboratory technique where plant material is placed in a chamber, and a solvent is heated and continuously cycled through the material. This method is ideal for thoroughly extracting fat-soluble compounds.
Advantages: Ensures complete extraction of active compounds with minimal solvent use.
Common Applications: High-performance oil-based extracts for serums or moisturisers.
Example: Extracting turmeric for its antioxidant-rich oil.
10. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
This modern technique uses microwave energy to rapidly heat the plant material and solvent, improving the efficiency of the extraction process. MAE is particularly effective for herbs with high moisture content.
Advantages: Fast, energy-efficient, and preserves delicate compounds.
Common Applications: Extracting antioxidants and essential oils for use in serums and creams.
Example: Microwave-assisted extraction of green tea for its potent antioxidants.
Comparison of the Extraction Techniques
Here’s a quick summary of when and why you might choose each method:
| Technique | Best For | Advantages |
| Maceration | Home or small-scale DIY | Easy, low-tech |
| Distillation | Essential oils and hydrosols | Captures volatile compounds |
| Cold Pressing | Carrier oils | Preserves nutrients and antioxidants |
| Supercritical CO2 | Premium, pure extracts | High potency, eco-friendly |
| Infusion | General-purpose, lightweight extracts | Gentle, easy to perform |
| Digestion | Heat-stable compounds | Gentle, efficient |
| Decoction | Tough materials (roots, seeds) | Ideal for concentrated extracts |
| Percolation | Fast extraction of powders | Highly concentrated extracts |
| Soxhlet Extraction | Complete fat-soluble extraction | High efficiency, minimal solvent waste |
| Microwave-Assisted | Moisture-rich plant material | Fast, preserves delicate compounds |
- Many modern skincare actives started as herbal remedies. For example, willow bark (a natural source of salicylic acid) and licorice root (known for brightening and soothing) have been used for centuries in traditional medicine—and are now found in cutting-edge formulations!
Benefits of Herbal Extracts in Skincare
Herbal extracts have become indispensable in modern skincare for their natural origin, efficacy, and ability to cater to diverse skin needs. Packed with bioactive compounds, they offer numerous advantages that can transform a skincare routine into a holistic self-care ritual. Below are the detailed benefits of using herbal extracts in skincare:
1. Rich in Antioxidants
Herbal extracts are a powerhouse of antioxidants, including flavonoids, polyphenols, and vitamins such as C and E. These compounds combat free radicals, which are unstable molecules that damage skin cells and accelerate ageing. By neutralising oxidative stress, antioxidants help to maintain youthful, radiant skin and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. For example, extracts like green tea, pomegranate, and rosemary are especially effective in protecting the skin from environmental damage caused by pollution and UV exposure.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Many herbal extracts, such as chamomile, calendula, and liquorice root, are celebrated for their anti-inflammatory effects. They soothe redness, calm irritation, and reduce swelling, making them ideal for sensitive or reactive skin. These extracts work by inhibiting inflammatory pathways in the skin, offering relief from conditions like eczema, rosacea, and acne. Their gentle nature makes them a preferred choice for daily skincare formulations.
3. Hydration and Moisture Retention
Certain herbal extracts, such as aloe vera and cucumber, are naturally hydrating. They contain humectants and polysaccharides that draw water to the skin and lock in moisture. These ingredients help restore the skin’s natural barrier, preventing dryness and dehydration. Herbal extracts rich in mucilage, such as marshmallow root, create a protective film over the skin, leaving it plump and soft.
4. Brightening and Skin Tone Improvement
Herbal extracts like liquorice root, bearberry, and mulberry are widely popular for their skin-brightening properties. They help inhibit melanin production by targeting the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a crucial role in pigmentation. Regular use of products containing these extracts can diminish dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and uneven skin tone, giving the skin a luminous appearance without harsh chemicals.
5. Anti-Ageing Benefits
Herbal extracts are rich in compounds that stimulate collagen production, improve skin elasticity, and reduce the appearance of fine lines. For instance, extracts like ginseng and centella asiatica (gotu kola) promote cell regeneration and strengthen the skin structure. These botanicals help prevent premature ageing by keeping the skin firm, smooth, and resilient.
6. Acne Prevention and Control
Many herbal extracts have antibacterial and antifungal properties, which make them effective in combating acne-causing bacteria. Tea tree oil, neem, and willow bark extract are particularly popular for their ability to cleanse the skin, reduce sebum production, and prevent breakouts. They also work to soothe inflammation associated with acne, helping the skin heal faster.

7. Detoxification and Purification
Herbal extracts like green tea, dandelion, and burdock root are popular for their detoxifying properties. They help flush out toxins from the skin, unclog pores, and improve circulation, leading to a clearer, more radiant complexion. These extracts also enhance the skin’s natural detoxification processes, which can become sluggish due to environmental stressors and lifestyle factors.
8. Wound Healing and Repair
Herbal extracts such as calendula, centella asiatica, and aloe vera accelerate wound healing by stimulating cell proliferation and tissue repair. These extracts are often in products for post-treatment care, minor cuts, or sunburn relief. They enhance the skin’s recovery while minimising scarring, making them invaluable in restorative skincare formulations.
9. Antimicrobial and Antifungal Protection
Certain herbal extracts, like oregano, thyme, and eucalyptus, have potent antimicrobial and antifungal properties. These extracts create a protective barrier against harmful microbes, reducing the risk of skin infections. They are frequently in products for oily or acne-prone skin and are also in formulations for foot care and scalp treatments.
10. Versatility Across Skin Types
One of the key benefits of herbal extracts is their adaptability. With such a wide variety of options available, there are extracts suitable for every skin type and concern. For example, rose extract and chamomile are gentle enough for sensitive skin, while witch hazel and tea tree are effective for oily and acne-prone skin. This versatility makes herbal extracts a cornerstone of personalised skincare.
11. Environmental and Ethical Appeal
Herbal extracts align with the growing demand for sustainable and natural skincare solutions. Many extracts derive from renewable resources and are biodegradable, reducing the environmental impact. Additionally, their use often supports ethical sourcing practices, making them an attractive option for conscious consumers.
12. Synergistic Effects
When combined, herbal extracts can offer synergistic benefits, enhancing each other’s efficacy. For instance, pairing aloe vera with green tea can maximise hydration while boosting antioxidant protection. This combinatory potential makes them a favourite choice for formulating complex skincare products that address multiple concerns simultaneously.
The Most Common Herbal Extracts Used in Skincare
Herbal extracts are essential in skincare, providing a variety of benefits ranging from hydration and brightening to soothing and repairing the skin. Each extract has unique bioactive compounds that target specific concerns, making them versatile and highly sought-after in both traditional and modern formulations. Below is an expanded discussion of some of the most common herbal extracts in skincare:
1. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is one of the most popular herbal extracts in skincare, popular for its soothing and hydrating properties. Packed with vitamins (A, C, and E), antioxidants, enzymes, and amino acids, aloe vera is highly effective in calming irritation, reducing redness, and healing wounds or sunburns. Its humectant properties make it excellent for maintaining hydration and restoring the skin barrier, making it a staple ingredient in products for sensitive and dry skin. It is also gentle enough for people with acne-prone skin, helping to reduce inflammation without clogging pores.
2. Green Tea
Green tea extract is a powerful antioxidant-rich ingredient that protects the skin from environmental damage caused by free radicals. It contains polyphenols, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which reduce inflammation and combat signs of ageing. Green tea is also popular for its ability to regulate sebum production, making it a popular choice for oily and acne-prone skin. Products like toners, serums, and masks often feature green tea for its detoxifying and soothing properties.
3. Chamomile
Chamomile extract is famous for its calming and anti-inflammatory effects, making it ideal for sensitive or reactive skin. It contains bisabolol and chamazulene, which help soothe irritation, reduce redness, and promote skin healing. Chamomile is also an antioxidant, protecting the skin from oxidative stress. It’s a common addition to cleansers, moisturisers, and products targeting conditions like eczema and rosacea.
4. Liquorice Root
Liquorice root extract is a potent skin-brightening agent that works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production. This makes it effective in fading hyperpigmentation, dark spots, and discolouration. It also has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, making it suitable for sensitive or acne-prone skin. Often included in serums and creams, liquorice root is a natural alternative to harsh chemical brighteners.
5. Calendula
Calendula, coming from marigold flowers, is known for its skin-soothing and healing properties. Rich in flavonoids and triterpenoids, calendula helps calm irritation, reduce redness, and accelerate wound healing. It is particularly effective in products for people with sensitive skin or post-procedure care. Calendula is also popular for its antimicrobial properties, making it a versatile ingredient in everything from face creams to lip balms.
6. Rose
Rose extract, including rose water and rose oil, is widely used for its hydrating, soothing, and anti-ageing benefits. Rich in vitamins C and E, rose helps improve skin texture, restore moisture, and combat dullness. Its gentle nature makes it suitable for sensitive skin, while its astringent properties help refine pores and balance oil production. Rose extract is commonly part of toners, facial mists, and serums.
Infusion:
A process of steeping herbs in hot water or oil to extract active ingredients, similar to making tea.
Tincture:
A concentrated liquid herbal extract made using alcohol or a mix of alcohol and water as a solvent.
Maceration:
A cold-extraction method where herbs are soaked in oil for an extended period to absorb their beneficial compounds.
Hydrosol:
Also known as floral water, it’s the aromatic water left behind after steam distilling plants (used in gentle skincare).
Adaptogen
Herbs that help the body adapt to stress and rebalance; some (like ashwagandha) are used in skincare for calming effects.
Phytochemicals:
Naturally occurring plant compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or skin-rejuvenating properties.
7. Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is a natural astringent popular for its ability to tighten pores, reduce inflammation, and control excess oil. It is rich in tannins, which provide antimicrobial and antioxidant benefits. Witch hazel is often present in toners, spot treatments, and cleansers for oily or acne-prone skin. However, it’s gentle enough for use in formulations for sensitive skin when properly diluted.
8. Tea Tree
Tea tree extract is a potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory ingredient that is especially effective for treating acne. Its ability to kill bacteria and reduce swelling makes it a common inclusion in spot treatments, cleansers, and masks. Tea tree is also beneficial for soothing irritation and addressing fungal skin conditions, such as dandruff or athlete’s foot.
9. Centella Asiatica (Gotu Kola)
Centella asiatica is a star ingredient in Korean skincare, popular for its remarkable skin-healing properties. It promotes collagen production, improves skin elasticity, and strengthens the skin barrier. Rich in triterpenoids and amino acids, Centella asiatica is also an excellent choice for calming inflammation and redness, making it a staple in products for sensitive and damaged skin.
10. Turmeric
Turmeric is a powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich herb that has been used for centuries in Ayurvedic skincare. Its active compound, curcumin, helps brighten the skin, reduce acne scars, and combat signs of ageing. Turmeric is also effective in treating hyperpigmentation and soothing irritation, making it a versatile ingredient in face masks, creams, and serums.
11. Rosemary
Rosemary extract is a multitasking ingredient with antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps protect the skin from environmental stressors, reduces puffiness, and improves circulation for a glowing complexion. Rosemary is particularly useful in formulations for oily or acne-prone skin due to its ability to control sebum production and fight bacteria.
12. Ginseng
Ginseng is a traditional herbal remedy famous for its anti-ageing properties. It stimulates collagen production, improves elasticity, and promotes cell regeneration, making it a favourite ingredient in serums and creams designed for mature skin. Ginseng also contains antioxidants that protect against environmental damage and brighten the skin, leaving it revitalised and radiant.
13. Cucumber
Cucumber extract is famous for its hydrating and cooling properties. Rich in vitamins C and K, it soothes irritation, reduces puffiness, and provides a refreshing effect. Cucumber is a popular choice in eye creams, gels, and masks, as well as hydrating mists and toners.
14. Lavender
The main use of lavender extract is consequence to its calming and anti-inflammatory benefits. It soothes irritated skin, helps treat acne, and reduces redness. Additionally, lavender has antimicrobial properties that promote healthy skin. It is often present in creams, facial oils, and products formulated for sensitive or acne-prone skin.
15. Sea Buckthorn
Sea buckthorn extract is a nutrient-rich ingredient full of vitamins, fatty acids, and antioxidants. It promotes skin regeneration, improves elasticity, and provides intense hydration. This extract is especially beneficial for dry or mature skin, as it nourishes and protects while enhancing the skin’s natural radiance.

Myths and Misconceptions About Herbal Extracts
Herbal extracts often enjoy a “natural halo,” which can be both a blessing and a source of confusion. Let’s demystify some of the most common misconceptions:
1. “Natural means always safe.”
This is one of the biggest myths in skincare. Just because an ingredient has a plant origin doesn’t guarantee it’s suitable for all skin types. Poison ivy is natural too — but you wouldn’t want it in your serum. Some herbal extracts, such as cinnamon or mint, can cause irritation or sensitisation in sensitive or allergy-prone skin. Always patch-test, and look for dermatologically tested formulas.
2. “All herbal extracts are created equal.”
The quality and effectiveness of an herbal extract depend on the extraction method, concentration, and plant part used. For instance, green tea extract might have different antioxidant levels depending on whether it has leaves or stems origins, and whether the process uses alcohol or glycerin.
3. “Herbal = organic.”
Many consumers assume herbal ingredients are organic and processed without chemicals. In reality, unless certified, herbal ingredients may come from conventional farming using pesticides. Look for certifications like COSMOS Organic or ECOCERT if organic sourcing matters to you.
4. “They don’t deliver ‘real’ results.”
Some herbal ingredients have centuries of anecdotal evidence and growing clinical data behind them. For example, Centella Asiatica and liquorice root have been studied for their anti-inflammatory and skin-brightening effects. Modern formulations combine traditional herbal wisdom with scientific precision to deliver measurable results.
5. “They’re only for people who prefer ‘natural’ beauty.”
While herbal skincare was once niche, today it’s mainstream. Herbal actives are often present in high-tech skincare products, including anti-ageing serums, barrier creams, and even clinical-grade treatments. They’re no longer just for natural or holistic beauty fans — they’re now a key player in modern dermocosmetic science.

Conclusion
Herbal extracts combine nature’s wisdom with scientific innovation, offering effective and gentle solutions for all skin types. Whether you’re battling dryness, dullness, or irritation, these plant-based powerhouses have something to offer.
Next time you shop for skincare, check the ingredient list for these extracts—they might be the key to your healthiest, most radiant skin yet!


Bear in mind that some of the links in this post are affiliate links and if you go through them to make a purchase I will earn a commission. Keep in mind that I link these companies and their products because of their quality and not because of the commission I receive from your purchases. The decision is yours, and whether or not you decide to buy something is completely up to you.





